VRF - Virtual Routing Forwarding
Virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) is a technology included in IP (Internet Protocol) network routers that allows multiple instances of a routing table to exist in a router and work simultaneously. This increases functionality by allowing network paths to be segmented without using multiple devices. Because traffic is automatically segregated, VRF also increases network security and can eliminate the need for encryption and authentication. Internet service providers (ISPs) often take advantage of VRF to create separate virtual private networks (VPNs) for customers; thus the technology is also referred to as VPN routing and forwarding.
The VRF device combined with ip rules provides the ability to create virtual routing and forwarding domains (aka VRFs, VRF-lite to be specific) in the Linux network stack. One use case is the multi-tenancy problem where each tenant has their own unique routing tables and in the very least need different default gateways.
VRF acts like a logical router, but while a logical router may include many routing tables, a VRF instance uses only a single routing table. In addition, VRF requires a forwarding table that designates the next hop for each data packet, a list of devices that may be called upon to forward the packet, and a set of rules and routing protocols that govern how the packet is forwarded. These tables prevent traffic from being forwarded outside a specific VRF path and also keep out traffic that should remain outside the VRF path.
VRFs are the same methods of network isolation/virtualization as VLANs. VLANs are used at the L2 and VRFs are L3 tools.VRFs are to routing table like VLANs are to LANs. Using VRFs, we are virtualizing routing table into multiple routing tables, similarly to VLANs used to virtualize LANs. One could say that VLANs are performing L2 virtualization, VRFs are performing L3 virtualization. VLANs make a single switch look like several switches; VRFs make a single router look like several routers.
VRF devices allow VRFs to be nested within namespaces. For example network namespaces provide separation of network interfaces at the device layer, VLANs on the interfaces within a namespace provide L2 separation and then VRF devices provide L3 separation.
What are the Security in VRF?
VRF also increases network security and can eliminate the need for encryption and authentication. Internet service providers (ISPs) often take advantage of VRF to create separate virtual private networks (VPNs) for customers; thus the technology is also referred to as VPN routing and forwarding.
VRF based network design uses 802.1q trunks protocol, GRE tunnels, or MPLS tags to extend and tie the VRFs together.
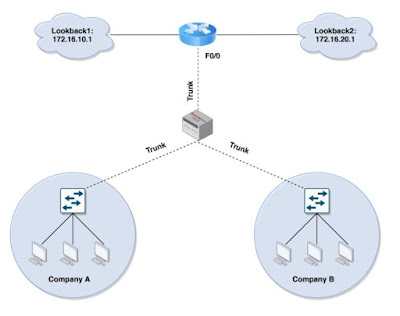
Example of VRF with Basic Confiuration:
Follow below commands to do the basiuc configuration:
!
ip vrf NTW-mgmt
rd 100:100
rt export 100:100
rt import 100:100
!
ip vrf NTW-sales
rd 200:200
rd both 200:200 (export and import)
!
Under the interface:
!
int ge0/1
ip vrf forwarding NTW-sales
ip address 172.16.10.1 255.255.255.0
!
int ge0/2
ip vrf forwarding NTW-mgmt
ip address 172.16.20.1 255.255.255.0
!
Virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) is a technology included in IP (Internet Protocol) network routers that allows multiple instances of a routing table to exist in a router and work simultaneously. This increases functionality by allowing network paths to be segmented without using multiple devices. Because traffic is automatically segregated, VRF also increases network security and can eliminate the need for encryption and authentication. Internet service providers (ISPs) often take advantage of VRF to create separate virtual private networks (VPNs) for customers; thus the technology is also referred to as VPN routing and forwarding.
 |
| VRF - Virtual Routing Forwarding |
VRF acts like a logical router, but while a logical router may include many routing tables, a VRF instance uses only a single routing table. In addition, VRF requires a forwarding table that designates the next hop for each data packet, a list of devices that may be called upon to forward the packet, and a set of rules and routing protocols that govern how the packet is forwarded. These tables prevent traffic from being forwarded outside a specific VRF path and also keep out traffic that should remain outside the VRF path.
VRFs are the same methods of network isolation/virtualization as VLANs. VLANs are used at the L2 and VRFs are L3 tools.VRFs are to routing table like VLANs are to LANs. Using VRFs, we are virtualizing routing table into multiple routing tables, similarly to VLANs used to virtualize LANs. One could say that VLANs are performing L2 virtualization, VRFs are performing L3 virtualization. VLANs make a single switch look like several switches; VRFs make a single router look like several routers.
VRF devices allow VRFs to be nested within namespaces. For example network namespaces provide separation of network interfaces at the device layer, VLANs on the interfaces within a namespace provide L2 separation and then VRF devices provide L3 separation.
What are the Security in VRF?
VRF also increases network security and can eliminate the need for encryption and authentication. Internet service providers (ISPs) often take advantage of VRF to create separate virtual private networks (VPNs) for customers; thus the technology is also referred to as VPN routing and forwarding.
VRF based network design uses 802.1q trunks protocol, GRE tunnels, or MPLS tags to extend and tie the VRFs together.
Example of VRF with Basic Confiuration:
Follow below commands to do the basiuc configuration:
!
ip vrf NTW-mgmt
rd 100:100
rt export 100:100
rt import 100:100
!
ip vrf NTW-sales
rd 200:200
rd both 200:200 (export and import)
!
Under the interface:
!
int ge0/1
ip vrf forwarding NTW-sales
ip address 172.16.10.1 255.255.255.0
!
int ge0/2
ip vrf forwarding NTW-mgmt
ip address 172.16.20.1 255.255.255.0
!
YquepiQcor-a_1998 Christina Love https://wakelet.com/wake/rCu9GcoKG5YktwKRbs8XR
ReplyDeletegenkahoge
Nriocapratne_Columbia Kayla Thompson Free Download
ReplyDeletescarsowalkllet