IP SLAs sends data across the network to measure performance between multiple network locations or across multiple network paths. It simulates network data and IP services and collects network performance information in real time.
IP SLAs generates and analyses traffic either between Cisco devices or from a Cisco device to a remote IP device such as a network application server. Cisco IP SLAs is Layer 2 transport independent, you can configure end-to-end operations over disparate networks to best reflect the metrics that an end user is likely to experience.
IP SLA is an active method of monitoring and reliably reporting on network performance. By "active," I refer to the fact that IP SLA will generate and actively monitor traffic continuously across the network.
Operations of IP SLA:
Target:
The ultimate destination of the packets created and sent by the source.
Operation:
The type of test being performed on the network.
IP SLAs are especially useful for wide area networks (WANs) that connect multiple geographies and needs to be monitored from one central location.
IP SLA can be configured in a multiple way that it can report on statistics such as:
IP SLAs is SNMP-accessible, it can also be used by performance-monitoring applications like IPM and other third-party Cisco partner performance management products.
You have to perform below tasks to implement IP SLAs network performance measure:
Configure IP SLA
IP SLAs generates and analyses traffic either between Cisco devices or from a Cisco device to a remote IP device such as a network application server. Cisco IP SLAs is Layer 2 transport independent, you can configure end-to-end operations over disparate networks to best reflect the metrics that an end user is likely to experience.
IP SLA is an active method of monitoring and reliably reporting on network performance. By "active," I refer to the fact that IP SLA will generate and actively monitor traffic continuously across the network.
Operations of IP SLA:
Source:
A device that creates and inserts IP SLA packets into the network. The source is where all IP SLA operation tests are initiated.
A device that creates and inserts IP SLA packets into the network. The source is where all IP SLA operation tests are initiated.
Target:
The ultimate destination of the packets created and sent by the source.
Operation:
The type of test being performed on the network.
IP SLAs are especially useful for wide area networks (WANs) that connect multiple geographies and needs to be monitored from one central location.
IP SLA can be configured in a multiple way that it can report on statistics such as:
- Jitter
- Response time
- Packet loss
- Voice Quality Scoring (MOS)
- Connectivity
- Server or website responses and downtime
- Delay
Although you do not need a Cisco Router at the other end of what you are monitoring, you are able to obtain a more detailed output if you do. This Cisco router is referred to as an IP SLA Responder.
IP SLAs operation, various network performance statistics are monitored within the Cisco device and stored in both command-line interface (CLI) and Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) MIBs.
IP SLAs packets have configurable IP and application layer options such as source and destination IP address, User Datagram Protocol (UDP)/TCP port numbers, a type of service (ToS) byte (including Differentiated Services Code Point [DSCP] and IP Prefix bits), Virtual Private Network (VPN) routing/forwarding instance (VRF), and URL web address.
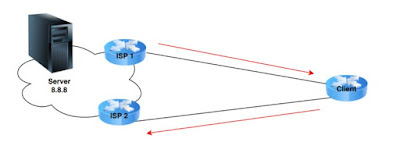
IP SLAs to monitor the performance between any area in the network with core, distribution, and edge without deploying a physical probe. It uses generated traffic to measure network performance between two networking devices. IP SLAs begins when the source device sends a generated packet to the destination device.
IP SLAs operation, various network performance statistics are monitored within the Cisco device and stored in both command-line interface (CLI) and Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) MIBs.
IP SLAs packets have configurable IP and application layer options such as source and destination IP address, User Datagram Protocol (UDP)/TCP port numbers, a type of service (ToS) byte (including Differentiated Services Code Point [DSCP] and IP Prefix bits), Virtual Private Network (VPN) routing/forwarding instance (VRF), and URL web address.
IP SLAs to monitor the performance between any area in the network with core, distribution, and edge without deploying a physical probe. It uses generated traffic to measure network performance between two networking devices. IP SLAs begins when the source device sends a generated packet to the destination device.
After the destination device receives the packet, depending on the type of IP SLAs operation, it responds with time-stamp information for the source to make the calculation on performance metrics. An IP SLAs operation performs a network measurement from the source device to a destination in the network using a specific protocol such as UDP.
IP SLAs is SNMP-accessible, it can also be used by performance-monitoring applications like IPM and other third-party Cisco partner performance management products.
You have to perform below tasks to implement IP SLAs network performance measure:
- Enable the IP SLAs responder, if required.
- We have to Configure any options available for the specified operation type.
- Needs to Configure the required IP SLAs operation type.
- It required need to configured threshold conditions.
- Display and interpret the results of the operation using the Cisco IOS CLI or a network management system (NMS) system with SNMP.
- Schedule the operation to run, then let the operation run for a period of time to gather statistics.
Configure IP SLA
While the time of configuring IP SLA, you have to specify the IP SLA operation number. The IP SLA operation number can be anywhere from 1 to 2147483647. Once the IP SLA operation number has been configured, you can select which type of IP SLA operation you want.
Configure an ICMP echo IP SLAs operation
Cisco(config)# ip sla 5
Cisco(config-ip-sla)# icmp-echo 172.16.10.49
Cisco(config-ip-sla-echo)# frequency 30
Cisco(config-ip-sla-echo)# exit
Cisco(config)# ip sla schedule 5 start-time now life forever
Cisco(config)# end
Configure an IP SLA CFM Probe or Jitter operation
Cisco(config)# ip sla 1
Cisco(config-ip-sla)# ethernet echo mpid 23 domain abc vlan 8
Cisco(config-ip-sla-ethernet-echo)# exit
Cisco(config)# ip sla schedule 1 start-time now
Configuration
Hopefully this blogs provided to you with a basic understanding of how IP SLA along with how it works and how it can be used to monitor your network and services. The configuration examples above show that what IP SLA is capable of performing.
Configure an ICMP echo IP SLAs operation
Cisco(config)# ip sla 5
Cisco(config-ip-sla)# icmp-echo 172.16.10.49
Cisco(config-ip-sla-echo)# frequency 30
Cisco(config-ip-sla-echo)# exit
Cisco(config)# ip sla schedule 5 start-time now life forever
Cisco(config)# end
Configure an IP SLA CFM Probe or Jitter operation
Cisco(config)# ip sla 1
Cisco(config-ip-sla)# ethernet echo mpid 23 domain abc vlan 8
Cisco(config-ip-sla-ethernet-echo)# exit
Cisco(config)# ip sla schedule 1 start-time now
Configuration
Hopefully this blogs provided to you with a basic understanding of how IP SLA along with how it works and how it can be used to monitor your network and services. The configuration examples above show that what IP SLA is capable of performing.
Comments
Post a Comment