DHCP is one of those basic fundamentals that all Systems and Network admins should have a firm grasp on. DHCP servers are responsible for providing PCs and devices on your network information such as IP addressing, the default gateway and DNS server information.
DHCP snooping is a DHCP security feature that provides security by filtering untrusted DHCP messages and by building and maintaining a DHCP snooping binding table. An untrusted message is a message that is received from outside the network or firewall and that can cause traffic attacks within your network.
The DHCP snooping binding table contains the MAC address, IP address, lease time, binding type, VLAN number, and interface information that corresponds to the local untrusted interfaces of a switch; it does not contain information regarding hosts interconnected with a trusted interface.
DHCP snooping acts like a firewall between untrusted hosts and DHCP servers. It also gives you a way to differentiate between untrusted interfaces connected to the end-user and trusted interfaces connected to the DHCP server or another switch.
DHCP Snooping Configuration with Switch
DHCP Snooping binding to Database- Dynamic ARP inspectionThe DHCP snooping binding table contains the MAC address, IP address, lease time, binding type, VLAN number, and interface information that corresponds to the local untrusted interfaces of a switch; it does not contain information regarding hosts interconnected with a trusted interface.
DHCP snooping acts like a firewall between untrusted hosts and DHCP servers. It also gives you a way to differentiate between untrusted interfaces connected to the end-user and trusted interfaces connected to the DHCP server or another switch.
DHCP snooping acts like a firewall between untrusted hosts and DHCP servers. It also gives you a way to differentiate between untrusted interfaces connected to the end-user and trusted interfaces connected to the DHCP server or another switch.
It also maintains a list of DHCP address bindings by inspecting traffic flowing between clients and the DHCP server, which provides certainty around who the real hosts are. The binding information collected by DHCP Snooping is used by other security features like IPSG and DAI.
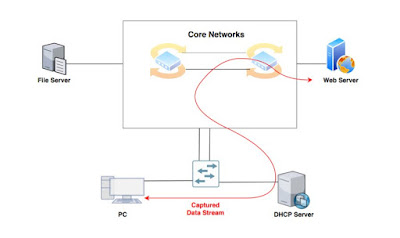
Our client connects to an untrusted port; all ports are untrusted by default. When the client machine sends a DHCPDISCOVER message with DHCP Snooping enabled, the switch will only send the DHCP broadcast message to trusted ports. In this case our distribution switch is acting as the DHCP server, but a DHCP server running external to the switch could also be used. A trusted port is the only port which is allowed to send DHCP Server responses such as DHCPOFFER.
DHCP Snooping Configuration with Switch
When you configure DHCP snooping on your switch, you are enabling the switch to differentiate untrusted interfaces from trusted interfaces. You must enable DHCP snooping globally before you can use DHCP snooping on a VLAN. You can enable DHCP snooping independently from other DHCP features.
Once you have enabled DHCP snooping, all the DHCP relay information option configuration commands are disabled; this includes the following commands:
ip dhcp relay information check
ip dhcp relay information policy
ip dhcp relay information trusted
ip dhcp relay information trust-all
How DHCP Snooping works?
ip dhcp relay information check
ip dhcp relay information policy
ip dhcp relay information trusted
ip dhcp relay information trust-all
How DHCP Snooping works?
DHCP Snooping is a Layer 2 security switch feature which blocks unauthorized (rogue) DHCP servers from distributing IP addresses to DHCP clients. In fact Cisco was the first vendor to implement DHCP Snooping as a security feature in its network switches and other vendors have since then followed with similar features.
The way DHCP Snooping works is fairly straight forward. DHCP Snooping categorizes all switchports into two simple categories:
- Trusted Ports
- Untrusted Ports
A Trusted Port, also known as a Trusted Source or Trusted Interface, is a port or source whose DHCP server messages are trusted because it is under the organization’s administrative control. For example, the port to which your organization’s DHCP server connects to is considered a Trusted Port. This is also shown in the diagram below:
Untrusted Port, also known as an Untrusted Source or Untrusted Interface, is a port from which DHCP server messages are not trusted. An example on an untrusted port is one where hosts or PCs connect to from which DHCP OFFER, DHCP ACK or DHCPNAK messages should never be seen as these are sent only by DHCP Servers.
Untrusted Port, also known as an Untrusted Source or Untrusted Interface, is a port from which DHCP server messages are not trusted. An example on an untrusted port is one where hosts or PCs connect to from which DHCP OFFER, DHCP ACK or DHCPNAK messages should never be seen as these are sent only by DHCP Servers.
DHCP Snooping is enabled it will begin to build a dynamic database containing an entry for each untrusted host with a leased IP address if the host is associated with a VLAN that has DHCP Snooping enabled. No entries are created for hosts connected to trusted interfaces.
Each entry in the binding database contains the following information:
- MAC address of the untrusted host
- Leased IP address of the untrusted host
- Lease time
- Binding type
- VLAN number & interface the untrusted host is associated with
As untrusted hosts are assigned IP addresses from the trusted DHCP server the switch will automatically create new entries, update and cleanup the DHCP Snooping Binding Database.
For example, when an IP address lease expires or the switch receives a DHCPRELEASE message from the untrusted host, it will remove the specific entry from the database. On the other hand an entry will be created in the database if the switch sees a DHCPACK message from the trusted DHCP server acknowledging the assignment of an IP address to an untrusted host.
Conclusion:
The DHCP simplifies the IP addressing, it raises security concerns at the same time. To address the concerns, DHCP Snooping, one of the protection mechanisms can prevent the invalid DHCP addresses from the rogue DHCP server and can ward off the resource-exhausting attack that attempts to use up all existing DHCP addresses.
Conclusion:
The DHCP simplifies the IP addressing, it raises security concerns at the same time. To address the concerns, DHCP Snooping, one of the protection mechanisms can prevent the invalid DHCP addresses from the rogue DHCP server and can ward off the resource-exhausting attack that attempts to use up all existing DHCP addresses.
Comments
Post a Comment