Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) is a Cisco proprietary protocol that attempts to overcome the limitations of existing redundant router protocols by adding basic load balancing functionality. In addition to being able to set priorities on different gateway routers, GLBP allows a weighting parameter to be set.
 |
| Gateway Load Balancing Protocol |
GLBP allow automatic selection and simultaneous recovery from first hop router failures.
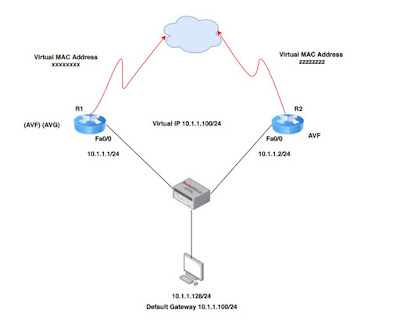
GLBP provides load balancing over multiple (router) gateways using a single virtual IP address and multiple virtual MAC addresses.
The bandwidth/traffic load is shared between multiple routers participating in the group rather than being handled by a single active router.
Configurations of GLBP:
- R2(config-if)#glbp 1 load-balancing ?
- host-dependent - Load balance equally, source MAC determines forwarder choice
- round-robin - Load balance equally using each forwarder in turn
- weighted - Load balance in proportion to forwarder weighting
Load Balancing of GLBP:
GLBP allows to Load balancing using three alogorithm:-
Round-Robin:
- This is the default type of GLBP algorithm.
- This algorithm is suitable for any number of hosts.
- AVG will assign the virtual Mac addresses serial wise, like first virtual Mac address is assigned to AVF1, then to AVF2 etc.
Host-dependent:
- particular host needs specific virtual Mac address every time then specific AVF is assigned to the hosts by the AVG.
- A given host is guaranteed to use the same Virtual Mac as long as number of VF’s in the GLBP group are constant.
- The Mac-address of the host is used to determine which AVF’s mac is the host directed towards.
- Host dependant GLBP is not recommended in situation where there are small number of hosts.
- The load will be distributed according to the requirement i.e assigning virtual Mac address in proportions. If we want some AVFs to handle more traffic than other, then change the weight.
- Each GLBP router in a group will advertise its weight and AVG will act based on that value.
- enable GLBP with glbp 1 load-balancing
- glbp 1 priority ( Higher is better, default is 100)
- glbp 1 ip xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx
- glbp 1 preempt < To enable preempt, by default its disabled>
- glbp 1 authentication ( Enabling authentication with in a group)
Authentications of GLBP
- No Authentication
- MG5 Authentication
- Plain text Authentication
Advantages of GLBP
- GLBP supports clear text and MD5 password Authentication.
- Allows load sharing using single virtual IP and multiple virtual Mac address.
- The main disadvantage of HSRP and VRRP is that only one gateway is elected to be the active gateway and used to forward traffic whilst the rest are unused until the active one fails.
- Gateway Load Balancing Protocol (GLBP) performs the similar function to HSRP and VRRP but it supports up to 1024 virtual routers load balancing among members in a GLBP group.
Comments
Post a Comment