DNS - Domain Name System
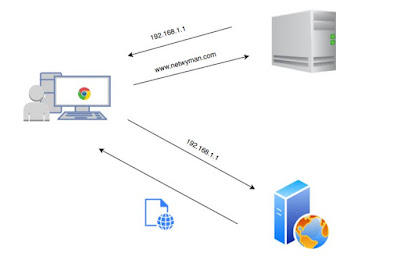
The DNS (domain name system) is a network system of servers that translates numeric IP addresses into readable, hierarchical Internet addresses, and vice versa. This is what allows your computer network to understand that you want to reach the server at 192.168.100.1 (for example) when you type into your browser a domain name such as www.netwyman.com
The task for DNS, Domain Name System, in this regard is to translate the domain name into an IP address. When a website is accessed a DNS lookup is performed which generates the IP address of the server hosting the website. A query is then sent to the IP address and the website comes back as the answer to the query.
DNS is used by virtually every device connected to the Internet, it is a common target of hacker attacks. Examples include DNS cache poisoning, DNS spoofing, and buffer overflow attacks transmitted through DNS commands.
There is two methods to control DNS traffic through your firewall: the DNS packet filter and the DNS Proxy policy. A packet filter examines the header information while a proxy examines the contents at the application layer and validates that the packet meets RFC compliance for DNS traffic. In this training module, we concentrate on the higher level of security available through a DNS Proxy policy.
To make configuration of your DNS security policy easy, the default configuration includes two template proxy actions for DNS. You can use these rulesets without changing them, or you can use the rulesets as a base for a ruleset to meet the needs of your organization.
This proxy action includes rulesets to protect your DNS server from DNS queries that are not correctly formed and certain query types that could be a risk to the security of your DNS server.
This proxy action includes rulesets to control outgoing DNS requests from your trusted users.
DNS Proxy
You can configure the firewall to act as a DNS server. First, create a DNS proxy and select the interfaces to which the proxy applies. Then specify the default DNS primary and secondary servers to which the firewall sends the DNS queries when it doesn’t find the domain name in its DNS proxy cache (and when the domain name doesn’t match a proxy rule).
To direct DNS queries to different DNS servers based on domain names, create DNS proxy rules. Specifying multiple DNS servers can ensure localization of DNS queries and increase efficiency. For example, you can forward all corporate DNS queries to a corporate DNS server and forward all other queries to ISP DNS servers.
Following are defines the DNS Proxy:
The DNS (domain name system) is a network system of servers that translates numeric IP addresses into readable, hierarchical Internet addresses, and vice versa. This is what allows your computer network to understand that you want to reach the server at 192.168.100.1 (for example) when you type into your browser a domain name such as www.netwyman.com
 |
| DNS - Domain Name System |
The task for DNS, Domain Name System, in this regard is to translate the domain name into an IP address. When a website is accessed a DNS lookup is performed which generates the IP address of the server hosting the website. A query is then sent to the IP address and the website comes back as the answer to the query.
DNS is used by virtually every device connected to the Internet, it is a common target of hacker attacks. Examples include DNS cache poisoning, DNS spoofing, and buffer overflow attacks transmitted through DNS commands.
There is two methods to control DNS traffic through your firewall: the DNS packet filter and the DNS Proxy policy. A packet filter examines the header information while a proxy examines the contents at the application layer and validates that the packet meets RFC compliance for DNS traffic. In this training module, we concentrate on the higher level of security available through a DNS Proxy policy.
To make configuration of your DNS security policy easy, the default configuration includes two template proxy actions for DNS. You can use these rulesets without changing them, or you can use the rulesets as a base for a ruleset to meet the needs of your organization.
DNS-Incoming:
This proxy action includes rulesets to protect your DNS server from DNS queries that are not correctly formed and certain query types that could be a risk to the security of your DNS server.
DNS-Outgoing:
This proxy action includes rulesets to control outgoing DNS requests from your trusted users.
DNS Proxy
You can configure the firewall to act as a DNS server. First, create a DNS proxy and select the interfaces to which the proxy applies. Then specify the default DNS primary and secondary servers to which the firewall sends the DNS queries when it doesn’t find the domain name in its DNS proxy cache (and when the domain name doesn’t match a proxy rule).
To direct DNS queries to different DNS servers based on domain names, create DNS proxy rules. Specifying multiple DNS servers can ensure localization of DNS queries and increase efficiency. For example, you can forward all corporate DNS queries to a corporate DNS server and forward all other queries to ISP DNS servers.
Following are defines the DNS Proxy:
Static Entries:
Allows you to configure static FQDN-to-IP address mappings that the firewall caches and sends to hosts in response to DNS queries.
DNS Proxy Rules:
Allows you to specify domain names and corresponding primary and secondary DNS servers to resolve queries that match the rule. If the domain name isn’t in the DNS proxy cache, the firewall searches for a match in the DNS proxy (on the interface on which the query arrived), and forwards the query to a DNS server based on the match results. If no match results, the firewall sends the query to the default DNS primary and secondary servers. You can enable caching of domains that match the rule.
Advanced:
Allows you to enable caching and control TCP queries and UDP Query Retries. The firewall sends TCP or UDP DNS queries through the configured interface. UDP queries switch over to TCP when a DNS query response is too long for a single UDP packet.
Additional actions of DNS Proxy
Modify:
To modify a DNS proxy, click into the name of the DNS proxy configuration.
Delete:
Select a DNS proxy entry and click
Delete to remove the DNS proxy configuration.
Disable:
To disable a DNS proxy, click into the name of the DNS proxy entry and clear the
Enable option. To enable a DNS proxy that is disabled, click into the name of the DNS proxy entry and select Enable.
Cisco Umbrella
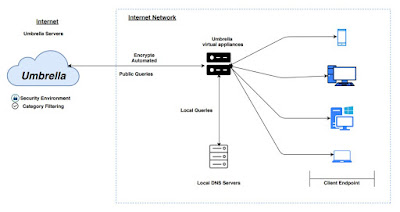
Most of the people knows that Cisco claims Umberella as the first line of defence against threats on the internet wherever user goes. Through analyzing and learning from IoT patterns, the Cisco Umbrella automatically uncover the attackers infrastructure staged for current and emerging threats.
 |
| Cisco Umbrella |
Collecting intelligence on advanced attacks that target your network is vibrant, but we need a way to easily enforce that intelligence. Umbrella blocks new threats beyond the network perimeter everywhere your employees work. Because Umbrella is built into the foundation of the Internet and delivered from the cloud, it provides complete visibility into Internet activity across all locations and users.
Through integration partnerships, Umbrella extends and enforces the local intelligence from your existing security stack to protect employees, whether they’re working on or off the corporate network. Most security integrations involve custom development and many hours of professional services. Not with Umbrella. In minutes, your local intelligence about malicious domains is extended to protect users beyond your perimeter.
Benefits of Cisco Umbrella:
- Serves as the first line of defense, so security teams will have fewer malware infections to remediate and threats will be stopped before they cause damage.
- Contains command and control callbacks over any port or protocol and provides real-time reports on that activity.
- Provides crucial visibility for incident response and also gives you confidence that you’re seeing everything.
- Provides visibility into sanctioned and unsanctioned cloud services in use across the enterprise, so you can uncover new services being used, see who is using them, and identify potential risk.
Features of Cisco Umbrella:
Anycast routing:
Requests are transparently sent to the fastest available node and automatically re-routed in the event of downtime. There is no added latency compared to your current service provider or local server. Many customers even experience a boost to their Internet speed. Add security without latency.
Umbrella Investigate:
Use the Investigate web-based console or API for access to Umbrella’s threat intelligence on domains, IPs, and malware across the Internet. Gain context about what Umbrella is blocking.
IP-layer enforcement:
Umbrella provides IP-layer enforcement on and off the corporate network using the roaming client or Cisco AnyConnect integration.DNS-layer enforcement:
The vast majority of Internet connections begin with a DNS request, and Umbrella uses that as the first point of inspection. Stop connections to malicious domains and IPs at the earliest point.
Intelligent proxy:
Using the Cisco Umbrella intelligent proxy, only requests to risky domains (those hosting malicious and legitimate content) are provided for deeper inspection, thereby removing performance impacts felt by traditional proxies.
Statistical and machine learning models:
Models are created to automatically score and classify our data so we can detect anomalies and uncover known and emergent threats.Packages of Cisco Umbrella:
Cisco Umbrella Platform:
The Platform package offers everything in the Insights package, plus prebuilt and custom API integrations and the ability to access threat intelligence in the Investigate web-based console for deeper context during investigations.
Cisco Umbrella Branch:
The Branch package is an entry-level cloud-delivered security service for the Cisco 4000 Series ISRs, which provide protection for guests and corporate users who are accessing the Internet at branch offices.
Cisco Umbrella Insights:
The Insights package offers everything in the Professional package plus user-based policies with Active Directory integration, URL and IP-layer enforcement, custom URL blacklists, file inspection using AV engines and Cisco AMP, the ability to retain logs indefinitely and advance reporting.
Cisco Umbrella Professional:
The Professional package offers a cloud security platform that provides protection against malware, phishing, and C2 callbacks when users are on and off the corporate network, in addition to web filtering and basic reporting.
Cisco Umbrella WLAN:
The Cisco Umbrella WLAN (wireless LAN) package is a cloud-delivered security service that provides protection for guests and corporate users who are accessing the Internet from wireless access points. Umbrella has been tightly integrated with the Cisco 2504, 5508, 5520, 8510, and 8540 wireless LAN controllers (WLCs) as well as the Wireless Services Module 2 (WiSM2)
Such an amazing article. I really enjoyed this article. Keep us updating with more interesting and informative articles. Also, Visit at Logiciel de sécurité DNS.
ReplyDeleteThank you very much for giving sometime and share your thoughts,
DeleteWe will keep sharing such a interesting and informative contents which will help to the whole industry.
Regards,
Netwyman
YsencamFqui_wa Julie Black https://wakelet.com/wake/yjI2WfJGA-4TVAp_O0kcP
ReplyDeletepierenmapa
curanaro_Kansas City Dana Jones Winamp Pro
ReplyDeleteLink
Speedify
nyatilimna
contculVtar-wo-1981 Brandy Sipes There
ReplyDeleteClick here
olsunveco