The Network Time Protocol (NTP) is a networking protocol for clock synchronization between computer systems over packet-switched, variable-latency data networks.
NTP is designed to synchronize the clocks on computers and networks across the Internet or Local Area Networks (LANs). NTP analyses the timestamp values including the frequency of errors and the stability. A NTP server will maintain an estimate of the quality of its reference clocks and of itself.
 |
| Network Time Protocol - NTP |
How to Synchronize NTP with time?
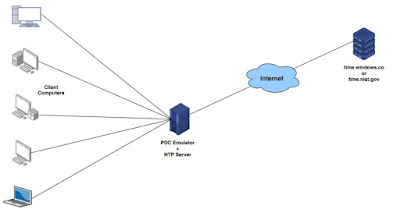
NTP server usually receives its time from a trustworthy time source, such as a radio clock attached to a time server, and then distributes this time across the network. NTP is extremely efficient and there is no more than one packet per minute is necessary to synchronize two machines to within a millisecond of each other
The NTP client initiates a time-request exchange with the NTP server. As a result of this exchange, the client is able to calculate the link delay and its local offset, and adjust its local clock to match the clock at the server's computer. As a rule, six exchanges over a period of about five to 10 minutes are required to initially set the clock.
Before synchronizing, NTP compares the time reported by several network devices and does not synchronize with one that is significantly different, even if it is a layer 1.
Let me talk about the Cisco devices Because Cisco NX-OS cannot connect to a radio or atomic clock and act as a layer 1 server, we recommend that you use the public NTP servers available on the Internet.
Once synchronized, the client updates the clock about once every 10 minutes, usually requiring only a single message exchange. In addition to client-server synchronization. This transaction occurs via the User Datagram Protocol on port 123. NTP also supports broadcast synchronization of peer computer clocks.
Features of NTP:
NTP servers, of which there are thousands around the world, have access to highly precise atomic clocks and GPS clocks. Specialized receivers are required to directly communicate with the NTP servers for these services. It is not practical or cost-effective to equip every computer with one of these receivers. Instead, computers designated as primary time servers are outfitted with the receivers, and they use protocols such as NTP to synchronize the clock times of networked computers.
NTP uses Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) to synchronize computer clock times with extreme precision, offering greater accuracy on smaller networks -- down to a single millisecond in a local area network and within tens of milliseconds over the internet. NTP does not account for time zones, instead relying on the host to perform such computations
Best Practices for NTP
- Use public NTP for external Hosts
- Configure your Internal NTP hierarchical service for your network
- Standardize to UTC time:
- Securing the Newtrok Time Service:
- Consider the business need for Cryptography:
NTP Startum levels:
Degrees of separation from the UTC source are defined as strata. A reference clock -- which receives true time from a dedicated transmitter or satellite navigation system -- is categorized as stratum-0; a computer that is directly linked to the reference clock is stratum-1; a computer that receives its time from a stratum-1 computer is stratum-2, and so on. Accuracy is reduced with each additional degree of separation.
NTP has known vulnerabilities. The protocol can be exploited and used in denial-of-service attacks for two reasons: First, it will reply to a packet with a spoofed source IP address; second, at least one of its built-in commands will send a long reply to a short request.
Importance of NTP
Accurate time across a network is important for many reasons; discrepancies of even fractions of a second can cause problems.
- Scheduled Data Backups
- Maintaining Network Accelerators
- Maintaining Network Management Systems
- Security Breach Analysis
- Compliance Regulations
- Maintaining Trading Systems
Configure NTP Server and Peer with IP Address
NTW# config t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL+Z.
NTW(config)# ntp server 192.0.2.105 key 42
NTW(config)# ntp peer 2001:420:c0c8:1003::217
NTW(config)# show ntp peers
II: Configuring NTP authentication
NTW(config)# ntp authentication-key 42 md5 aNiceKey
NTW(config)# show ntp authentication-keys
III. Authentication key MD5 String
NTW(config)# ntp trusted-key 42
NTW(config)# show ntp trusted-keys
Trusted Keys:42
NTW(config)# ntp authenticate
NTW(config)# show ntp authentication-status
Authentication enabled.
NTW(config)# ntp logging
NTW(config)# show ntp logging
Below example shows an NTP access group configuration with the following restrictions:
Peer restrictions are applied to IP addresses that pass the criteria of the access list named “aclpeer-NTW.”
Serve restrictions are applied to IP addresses that pass the criteria of the access list named “aclserve-NTW.”
Serve-only restrictions are applied to IP addresses that pass the criteria of the access list named “aclserve-only-NTW.”
Query-only restrictions are applied to IP addresses that pass the criteria of the access list named “aclquery-NTW.”
NTW# config t
NTW(config)# ntp peer 172.1.1.1
NTW(config)# ntp peer 172.2.2.2
NTW(config)# ntp peer 172.3.3.3
NTW(config)# ntp peer 172.4.4.4
NTW(config)# ntp peer 172.5.5.5
NTW(config)# ntp peer 172.6.6.6
NTW(config)# ntp peer 172.7.7.7
NTW(config)# ntp peer 172.8.8.8
NTW(config)# ntp access-group peer aclpeer-NTW
NTW(config)# ntp access-group serve aclserve-NTW
NTW(config)# ntp access-group serve-only aclserve-only-NTW
NTW(config)# ntp access-group query-only aclquery-NTW
NTW(config)# ip access-list aclpeer-NTW
NTW(config-acl)# 10 permit ip host 172.1.1.1 any
NTW(config-acl)# 20 permit ip host 10.8.8.8 any
NTW(config)# ip access-list aclserve-NTW
NTW(config-acl)# 10 permit ip host 172.4.4.4 any
NTW(config-acl)# 20 permit ip host 172.5.5.5 any
NTW(config)# ip access-list aclserve-only-NTW
NTW(config-acl)# 10 permit ip host 172.6.6.6 any
NTW(config-acl)# 20 permit ip host 172.7.7.7 any
NTW(config)# ip access-list aclquery-NTW
NTW(config-acl)# 10 permit ip host 172.2.2.2 any
NTW(config-acl)# 20 permit ip host 172.3.3.3 any
Comments
Post a Comment